
Thus, it is necessary to have sufficient knowledge about the distinct types of leadership styles. A leader can never rely on a single leadership style no one style is suitable for all kinds of situations that may arise in the workplace. Perhaps you’d be aware of some of them too. Also, there are some more aspects of leadership that can be covered but are not.There are a lot of different types of leadership styles or grids for various purposes to fulfill. The model ignores the importance of internal and external limits, matter and scenario. Limitations of Blake and Mouton’s Managerial Grid The training is aimed at basically helping leaders reach to the ideal state of 9, 9. This is done by administering a questionnaire that helps managers identify how they stand with respect to their concern for production and people. The Managerial or Leadership Grid is used to help managers analyze their own leadership styles through a technique known as grid training. Advantages of Blake and Mouton’s Managerial Grid A highly encouraging organisational climate of commitment, cooperation, trust and hope are created by the leader. An attempt is made to bring about an integration and harmony between the needs of people and of production. This is regarded as the most effective leadership. This is a safe style, not to push too much in either direction but to achieve a satisfactory balance between the requirements of production and of people. Moderate concern for production and people. Other considerations like people’s needs and satisfaction are secondary matters. His focus is on task performance by planning and controlling the production environment. In this combination, the leader swings to the other extreme and adopts a directive style to get his people work for the organisation. This is an antithesis of country club leadership. High concern for production and low concern for people. Such a leader gives little importance to production matters and work requirements of people. He tries to maintain friendly relations with people so that an amiable climate will motivate people to work with enthusiasm. In this combination, the leader takes great interest in keeping his people in good humour and in catering to their whims and needs. Low concern for production and high concern for people. They regard people as lazy and underdeveloped and hence think that no amount of leadership will change the frozen attitudes of people.

Their attitude towards getting things done from and maintaining relationships with people are casual and confused. In this combination, leaders (managers) are apathetic and irresponsible.
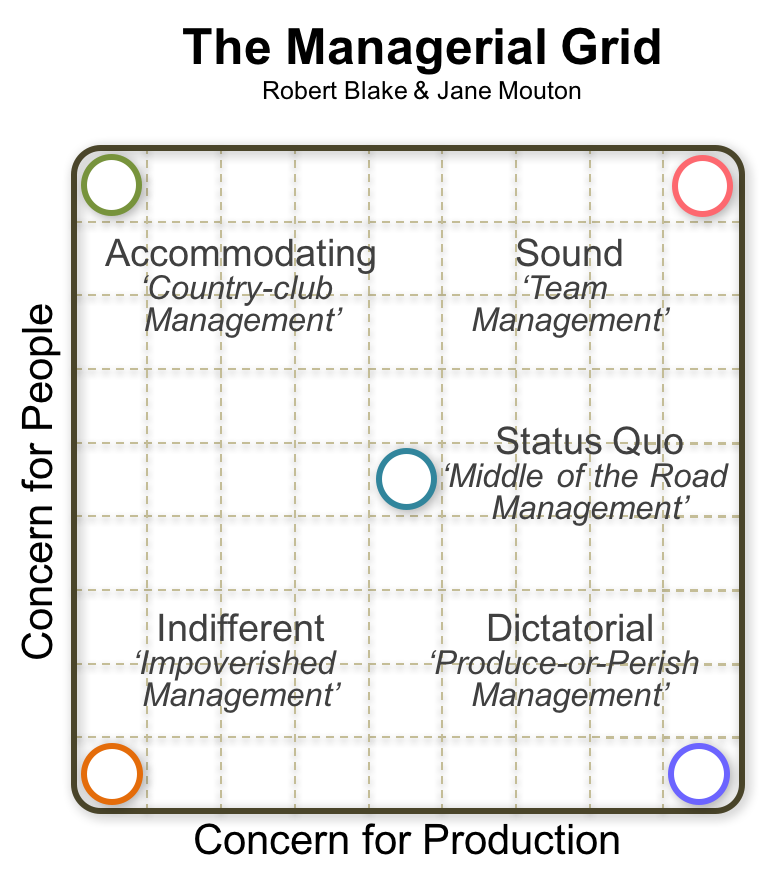
Low concern for production and for people. These five combinations are outlined as follows: Blake and Mouton argued that a leader’s managerial style is point on the grid they have identified five combinations of styles, for illustrative purposes out of 81 possible combinations. These are shown on horizontal and vertical dimensions of the grid on a 1 to 9 scales or degree. The two styles or orientations are: concern for production and concern for people. Many of the leadership studies conducted in the 1950’s at the University of Michigan and the Ohio State University focused on these two dimensions. The treatment of task orientation and people orientation as two independent dimensions was a major step in leadership studies. Mouton in the 1960s and has evolved in subsequent decades. The grid was originally developed by Robert R. The managerial grid model is a self-assessment tool by which individuals and organizations can help identify a manager’s or leader’s style.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
